Transcrocetin – a naturally occurring oxygenation enhancer.
Crocetin is a natural carotenoid and kosmotropic agent found in saffron and the cape jasmine plant.
TSC has been shown to transiently enhance oxygenation in plasma and interstitium.
OXYGENATION
TSC improves oxygenation in a rat ARDS model
INFLAMMATORY PATHWAYS
Crocetin surpasses NF-kB related inflammatory pathways in an ARDS model
HEMORRHAGIC SHOCK
TSC improves vital signs, organ function, and survival in a hemorrhagic shock rat model
ISCHEMIC STROKE
TSC improves oxygenation of brain tissue and reduces the size of infarct in rat and rabbit models of ischemic stroke
DAMAGE INHIBITION
Crocetin inhibits damage to the endothelium and reduce associated inflammation in HUVEC model
LPS-INDUCED ARDS
Crocetin improves the pulmonary vascular damage in the lungs of mice with LPS-induced ARDS and inhibit the inflammatory signaling pathways
-
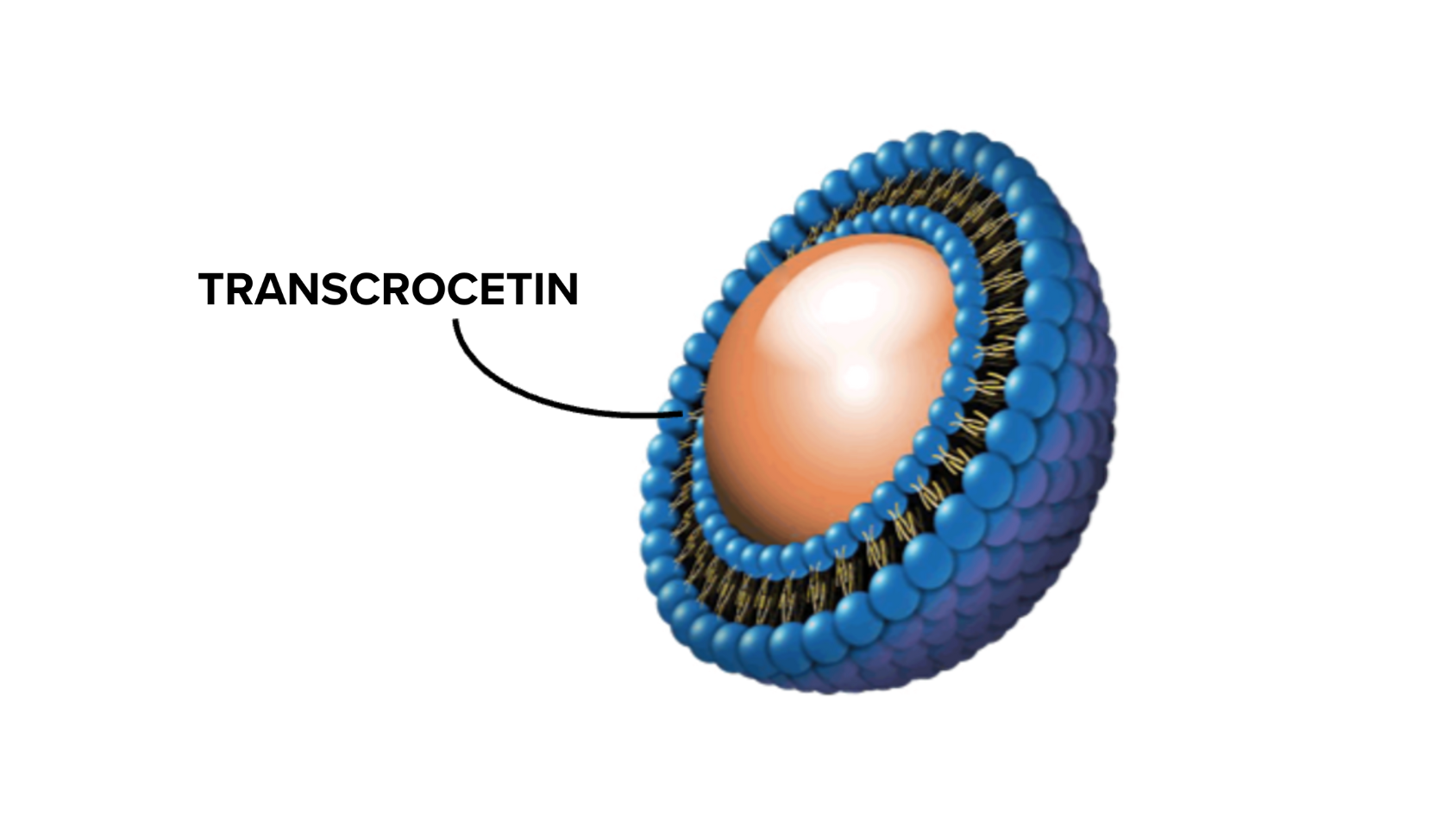
LEAF-4L6715 – Liposomal Formulation of TC Resolves Limitations of Free TC to Effectively Treat Hypoxia
Proprietary liposomal encapsulation design extends transcrocetin circulation and enables localized controlled release, enhancing living tissue oxygenation to overcome hypoxia.
SMALLEST BLOOD VESSELS
Prolonged circulation and controlled release increases accumulation in the smallest blood vessels (microcirculation within hypoxic tissues)
MICROCIRCULATORY TISSUE
Macrophage-assisted delivery enhances accumulation in remote hypoxic microcirculatory tissue and deep organ microenvironments
INCREASED RETENTION
Further retention of the medicine in the damaged microcirculatory tissue due to enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect
LEAF-4L6715
-
Origins
Free transcrocetin is a diterpenoid and natural carotenoid found in spices such as saffron, a constituent of the crocus flower and cape jasmine. Saffron, as a spice, has been consumed in many cultures for thousands of years.
-
Limitations
Therapeutic use of free transcrocetins has been limited by their
poor stability and low solubility which limits the bioavailability of transcrocetin. This is further compounded by a short in vivo half-life which limits the pharmacological effect of oxygenation. -
Design
LEAF-4L6715 is a carefully crafted liposomal formulation of transcrocetin achieved by entrapping a less soluble, divalent salt of transcrocetin inside the liposome. This construct facilitates the controlled release of transcrocetin from the liposome into blood circulation.
-
Impact
By releasing transcrocetin into circulation in a controlled manner, LEAF-4L6715 produces a more sustained oxygenation effect.
Transcrocetin – a naturally occurring oxygenation enhancer
Crocetin is a natural carotenoid and kosmotropic agent found in saffron and the cape jasmine plant. TSC has been shown to transiently enhance oxygenation in plasma and interstitium.
-
We’ve put a lot of thought in giving you the best possible experience to make your job easier.
-
Outstanding Support
Modules comes fully documented with step by step instructions + access to our premium support forum.
-
Simply Beautiful
Our themes are not just nicely coded, they are built to show your visitors how much you care for design.
-
Carefully Crafted
Coded with WordPress best practices in mind, Modules will give you an amazing looking site always.
-
20+ Builder Modules
Create as many modules as you want. Personalize them and build with them your pages.
-
WP Video Training
Enjoy a comprehensive collection of WordPress 101 video tutorials on our membership training area.
-
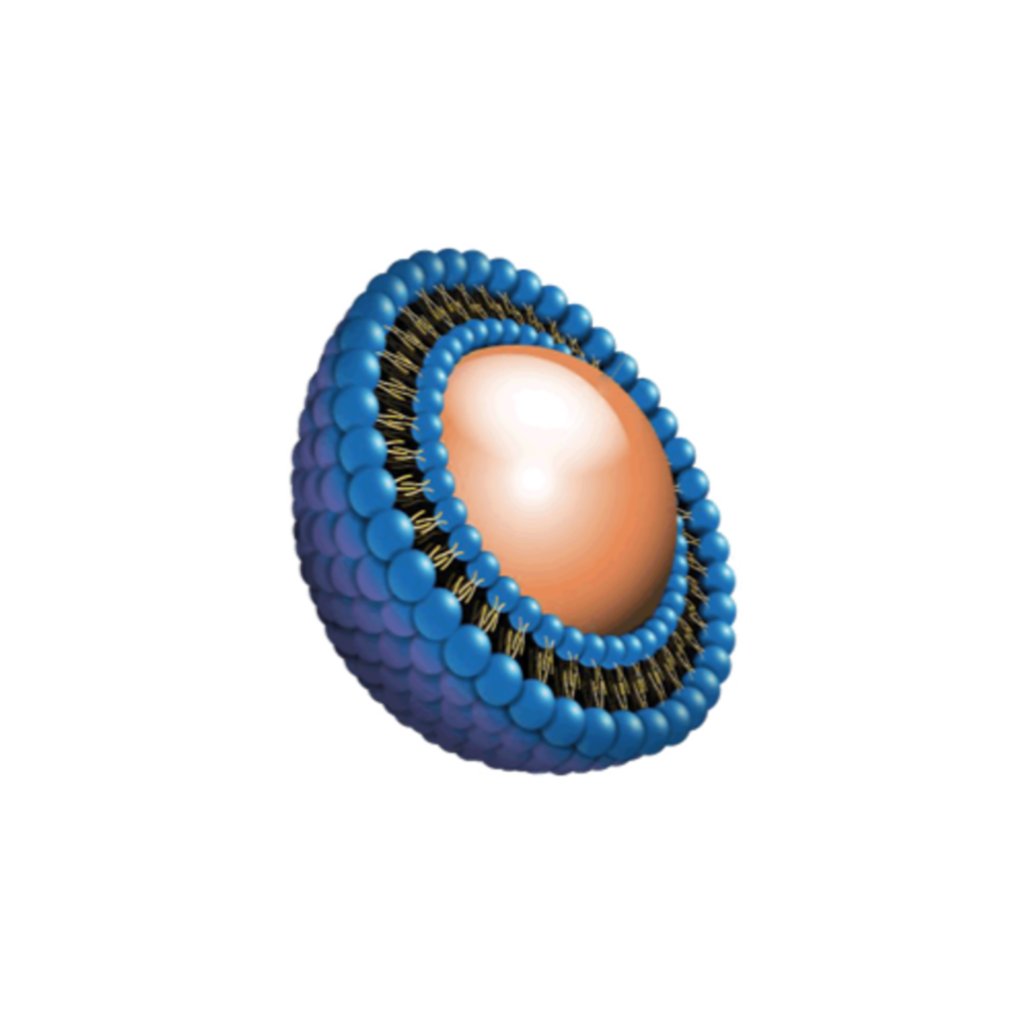
Mechanism of Action
Transcrocetin belongs to the class of molecules known as kosmotropes. The hallmark of kosmotropes is to alter the structure of water molecules in aqueous solutions such as water or blood. This altering creates channels through which smaller molecules such as oxygen and glucose can more easily travel to reach tissues where oxygen is needed.
- Proprietary nano liposomal encapsulation design extends transcroetin circulation and enables localized controlled release, enhancing living tissue oxygenation to overcome hypoxia
- Prolonged circulation and controlled release increases accumulation in the smallest blood vessels (microcirculation)
- Macrophage-assisted delivery enhances accumulation in remote hypoxic microcirculatory tissue and deep organ micro-environment
- Further retention of the medicine in the damaged microcirculatory tissue due to enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect
- Transcrocetin has been nicknamed “The Moses Molecule” because of its kosmotropic ability to part water
We Are Responding
LEAF-4L6715 is currently being studied in a Phase III registrational study in patients with ARDS in Europe via the Cardiovascular European Research Center (CERC).
LEAF-4L6715 has completed a Phase I/II trial showing promise in patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) due to COVID-19, Sepsis or other causes.
